
Use the information below to generate a citation. Then you must include on every digital page view the following attribution: If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a digital format, Then you must include on every physical page the following attribution: If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a print format, Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the We can see this by expanding out the general form and setting it equal to the standard form. The standard form and the general form are equivalent methods of describing the same function. Rewrite the equation in the form y a (x-h) 2 + k, where (h.

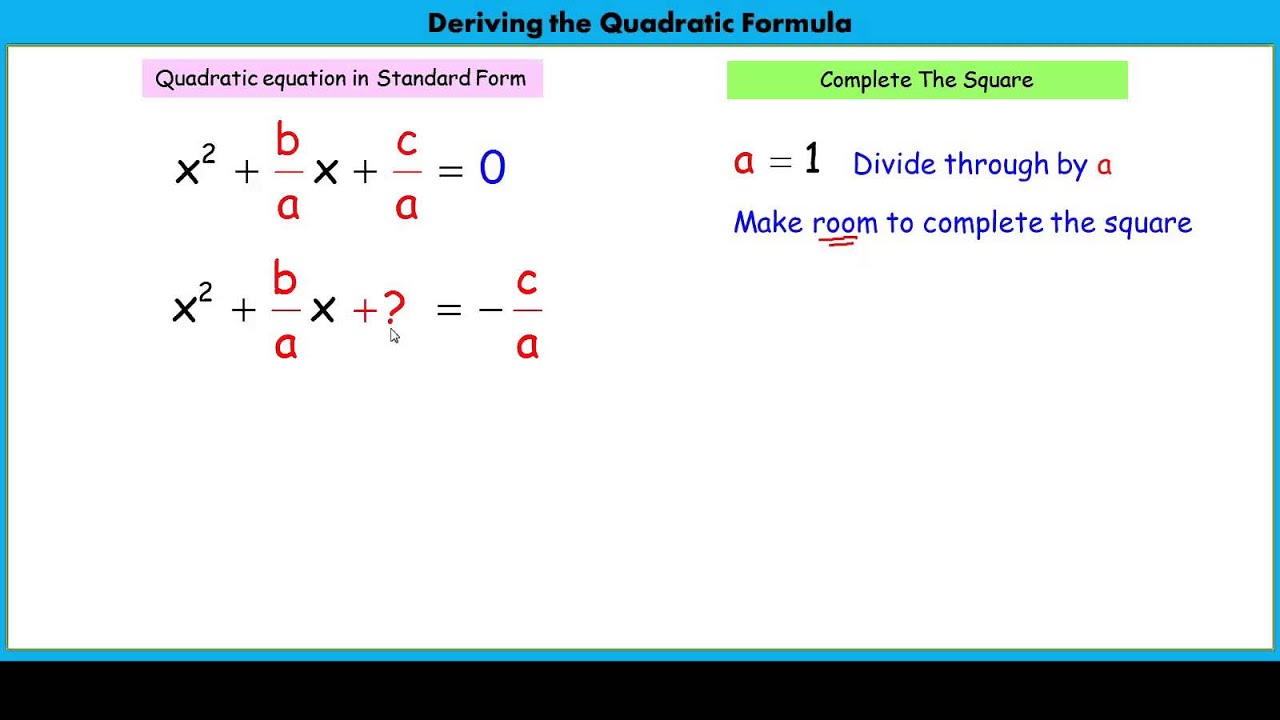
Simplify the equation by combining like terms on both sides. But if | a | 1, | a | > 1, so the graph becomes narrower. To convert a quadratic equation from standard form to vertex form, you can follow these steps: Rewrite the equation in the form y ax 2 + bx + c, where a, b, and c are the coefficients of the equation. If h > 0, h > 0, the graph shifts toward the right and if h 1, | a | > 1, the point associated with a particular x - x - value shifts farther from the x-axis, so the graph appears to become narrower, and there is a vertical stretch. If k > 0, k > 0, the graph shifts upward, whereas if k 0, k > 0, so the graph is shifted 4 units upward. The x - x - intercepts, those points where the parabola crosses the x - x - axis, occur at ( −3, 0 ) ( −3, 0 ) and ( −1, 0 ). For a parabola that opens upward, the vertex occurs at the lowest point on the graph, in this instance, ( −2, −1 ). The vertex always occurs along the axis of symmetry. This also makes sense because we can see from the graph that the vertical line x = −2 x = −2 divides the graph in half.
The axis of symmetry is x = − 4 2 ( 1 ) = −2. If a 0, a > 0, the parabola opens upward. If a > 0, a > 0, the parabola opens upward. Where a, b, a, b, and c c are real numbers and a ≠ 0. These features are illustrated in Figure 2.į ( x ) = a x 2 + b x + c f ( x ) = a x 2 + b x + c The graph is also symmetric with a vertical line drawn through the vertex, called the axis of symmetry. In either case, the vertex is a turning point on the graph. If the parabola opens down, the vertex represents the highest point on the graph, or the maximum value. If the parabola opens up, the vertex represents the lowest point on the graph, or the minimum value of the quadratic function.

One important feature of the graph is that it has an extreme point, called the vertex. The graph of a quadratic function is a U-shaped curve called a parabola. Working with quadratic functions can be less complex than working with higher degree functions, so they provide a good opportunity for a detailed study of function behavior. In this section, we will investigate quadratic functions, which frequently model problems involving area and projectile motion. The cross-section of the antenna is in the shape of a parabola, which can be described by a quadratic function. (credit: Matthew Colvin de Valle, Flickr)Ĭurved antennas, such as the ones shown in Figure 1, are commonly used to focus microwaves and radio waves to transmit television and telephone signals, as well as satellite and spacecraft communication. Some other quadratic polynomials have their minimum above the x axis, in which case there are no real roots and two complex roots.Figure 1 An array of satellite dishes. A quadratic polynomial with two real roots (crossings of the x axis) and hence no complex roots.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
